In addition to AI, there are several other closely related topics that are good to know. These include machine learning, data science, and deep learning.
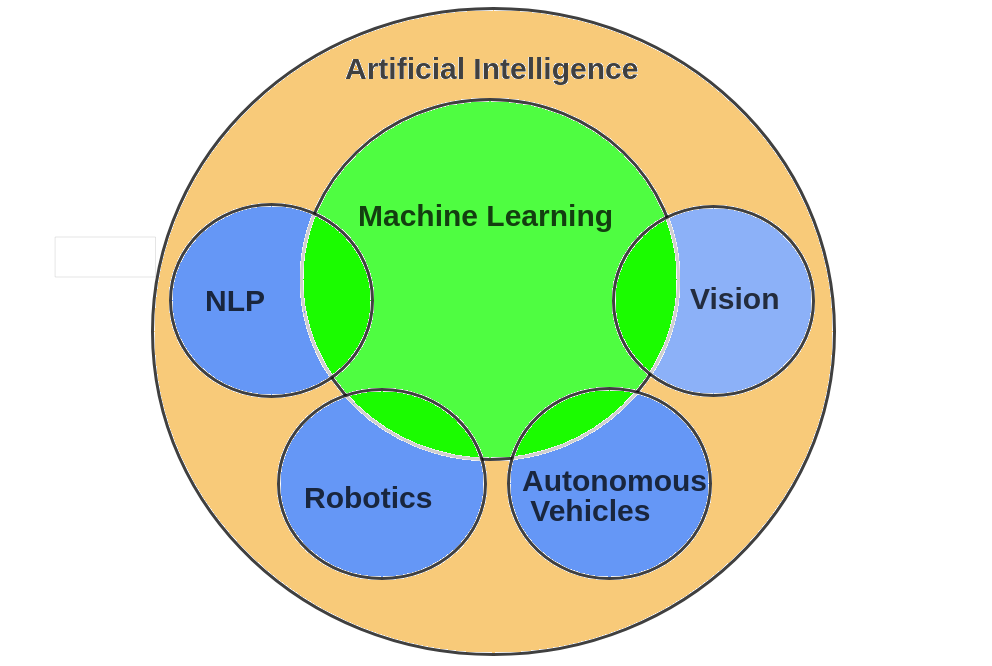
Machine learning can be said to be a sub-field of AI, which itself is a sub-field of computer science (such categories are often somewhat imprecise and some parts of machine learning could be equally well or better belong to statistics). Machine learning enables AI solutions that are adaptive. A concise definition can be given as follows:
Systems that improve their performance in a given task with more and more experience or data.
Deep learning is a sub-field of machine learning, which itself is a sub-field of AI, which itself is a sub-field of computer science. We will meet deep learning in some more detail in future posts, but for now let us just note that the “depth” of deep learning refers to the complexity of a mathematical model, and that the increased computing power of modern computers has allowed researchers to increase this complexity to reach levels that appear not only quantitatively but also qualitatively different from before. As you notice, science often involves a number of progressively more special sub-fields, sub-fields of sub-fields, and so on. This enables researchers to zoom into a particular topic so that it is possible to catch up with the ever increasing amount of knowledge accrued over the years, and produce new knowledge on the topic — or sometimes, correct earlier knowledge to be more accurate.

Data science is a recent umbrella term (term that covers several sub-disciplines) that includes machine learning and statistics, certain aspects of computer science including algorithms, data storage, and web application development. Data science is also a practical discipline that requires understanding of the domain in which it is applied in, for example, business or science: its purpose (what "added value" means), basic assumptions, and constraints. Data science solutions often involve at least a pinch of AI (but usually not as much as one would expect from the headlines).

Robotics means building and programming robots so that they can operate in complex, real-world scenarios. In a way, robotics is the ultimate challenge of AI since it requires a combination of virtually all areas of AI. For example:
- Computer vision and speech recognition for sensing the environment
- Natural language processing, information retrieval, and reasoning under uncertainty for processing instructions and predicting consequences of potential actions
- Cognitive modeling and affective computing (systems that respond to expressions of human feelings or that mimic feelings) for interacting and working together with humans
Many of the robotics-related AI problems are best approached by machine learning, which makes machine learning a central branch of AI for robotics.
0 comments:
Post a Comment