The most common machine learning algorithms are described below:
Linear Regression
It is one of the most well-known algorithms in statistics and machine learning.
Basic concept: Mainly linear regression is a linear model that assumes a linear relationship between the input variables say x and the single output variable say y. In other words, we can say that y can be calculated from a linear combination of the input variables x. The relationship between variables can be established by fitting a best line.
Basic concept: Mainly linear regression is a linear model that assumes a linear relationship between the input variables say x and the single output variable say y. In other words, we can say that y can be calculated from a linear combination of the input variables x. The relationship between variables can be established by fitting a best line.
Linear regression is of the following two types:
a. Simple linear regression: A linear regression algorithm is called simple linear regression if it is having only one independent variable.
b. Multiple linear regression: A linear regression algorithm is called multiple linear regression if it is having more than one independent variable.
Linear regression is mainly used to estimate the real values based on continuous variable(s). For example, the total sale of a shop in a day, based on real values, can be estimated by linear regression.
Logistic Regression
It is a classification algorithm and also known as logit regression. Mainly logistic regression is a classification algorithm that is used to estimate the discrete values like 0 or 1, true or false, yes or no based on a given set of independent variable. Basically, it predicts the probability hence its output lies in between 0 and 1.
Decision Tree
Decision tree is a supervised learning algorithm that is mostly used for classification problems.
Basically it is a classifier expressed as recursive partition based on the independent variables. Decision tree has nodes which form the rooted tree. Rooted tree is a directed tree with a node called “root”. Root does not have any incoming edges and all the other nodes have one incoming edge. These nodes are called leaves or decision nodes.
Basically it is a classifier expressed as recursive partition based on the independent variables. Decision tree has nodes which form the rooted tree. Rooted tree is a directed tree with a node called “root”. Root does not have any incoming edges and all the other nodes have one incoming edge. These nodes are called leaves or decision nodes.
Support Vector Machine (SVM)
It is used for both classification and regression problems. But mainly it is used for classification problems. The main concept of SVM is to plot each data item as a point in n-dimensional space with the value of each feature being the value of a particular coordinate. Here n would be the features we would have. Following is a simple graphical representation to understand the concept of SVM:
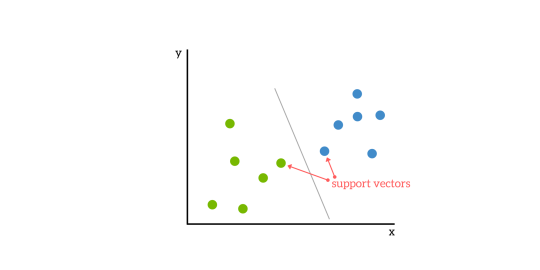
In the above diagram, we have two features hence we first need to plot these two variables in two dimensional space where each point has two co-ordinates, called support vectors. The line splits the data into two different classified groups. This line would be the classifier.
Naïve Bayes
It is also a classification technique. The logic behind this classification technique is to use Bayes theorem for building classifiers. The assumption is that the predictors are independent. In simple words, it assumes that the presence of a particular feature in a class is unrelated to the presence of any other feature. Below is the equation for Bayes theorem:
𝑃(𝐴|𝐵)=𝑃(𝐵|𝐴) 𝑃(𝐴)𝑃(𝐵)
The Naïve Bayes model is easy to build and particularly useful for large data sets.
K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN)
It is used for both classification and regression of the problems. It is widely used to solve classification problems. The main concept of this algorithm is that it used to store all the available cases and classifies new cases by majority votes of its k neighbors. The case being then assigned to the class which is the most common amongst its K-nearest neighbors, measured by a distance function. The distance function can be Euclidean, Minkowski and Hamming distance. Consider the following to use KNN:
It is used for both classification and regression of the problems. It is widely used to solve classification problems. The main concept of this algorithm is that it used to store all the available cases and classifies new cases by majority votes of its k neighbors. The case being then assigned to the class which is the most common amongst its K-nearest neighbors, measured by a distance function. The distance function can be Euclidean, Minkowski and Hamming distance. Consider the following to use KNN:
a. Computationally KNN are expensive than other algorithms used for classification problems.
b. The normalization of variables needed otherwise higher range variables can bias it.
c. In KNN, we need to work on pre-processing stage like noise removal.
b. The normalization of variables needed otherwise higher range variables can bias it.
c. In KNN, we need to work on pre-processing stage like noise removal.
K-Means Clustering
As the name suggests, it is used to solve the clustering problems. It is basically a type of unsupervised learning. The main logic of K-Means clustering algorithm is to classify the data set through a number of clusters. Follow these steps to form clusters by K-means:
a. K-means picks k number of points for each cluster known as centroids.
b. Now each data point forms a cluster with the closest centroids, i.e., k cluster
a. K-means picks k number of points for each cluster known as centroids.
b. Now each data point forms a cluster with the closest centroids, i.e., k cluster
c. Now, it will find the centroids of each cluster based on the existing cluster members.
d. We need to repeat these steps until convergence occurs.
d. We need to repeat these steps until convergence occurs.
Random Forest
It is a supervised classification algorithm. The advantage of random forest algorithm is that it can be used for both classification and regression kind of problems. Basically it is the collection of decision trees (i.e., forest) or you can say ensemble of the decision trees. The basic concept of random forest is that each tree gives a classification and the forest chooses the best classifications from them. Followings are the advantages of Random Forest algorithm:
a. Random forest classifier can be used for both classification and regression tasks.
b. They can handle the missing values.
c. It won’t over fit the model even if we have more number of trees in the forest.
a. Random forest classifier can be used for both classification and regression tasks.
b. They can handle the missing values.
c. It won’t over fit the model even if we have more number of trees in the forest.
0 comments:
Post a Comment